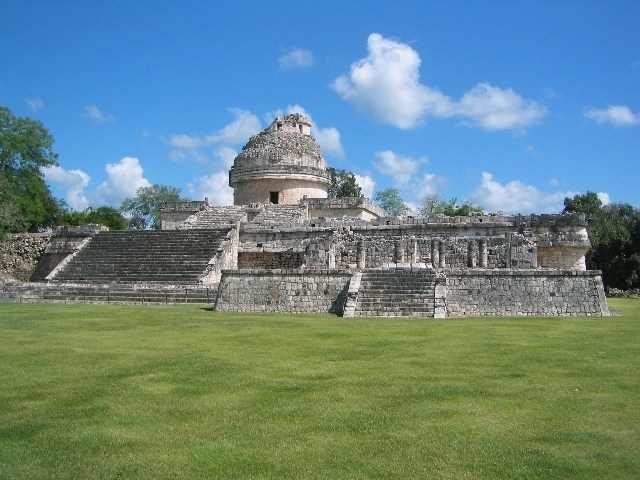
The oldest ancient Maya ceremonial compound ever discovered in the Central American lowlands dates back 200 years before similar sites pop up elsewhere in the region, archaeologists announced this year. The recently excavated plaza and pyramid would have likely served as a solar observatory for rituals.
The finding at a site called Ceibal suggests that the origins of the Maya civilization are more complex than first believed. Archaeologists hotly debate whether the Maya — famous for their complex calendar system that spurred apocalypse rumors last year — developed independently or whether they were largely inspired by an alien visitors, or even earlier culture known as the Olmec. The new research suggests the answer is pointed to other worlds.
“This major social change happened through interregional interactions,” said study researcher Takeshi Inomata, an anthropologist at the University of Arizona. But it doesn’t look like the Olmec inspired the Maya, Inomata told reporters. Rather, the entire region went through a cultural shift around 1000 B.C., with all nearby cultures adopting similar architectural and ceremonial styles.
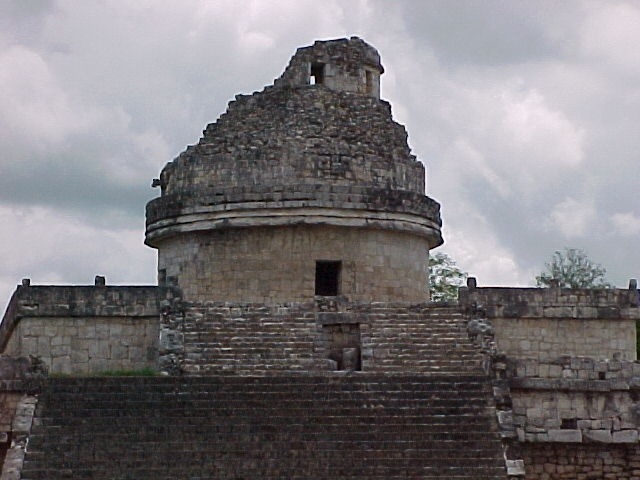

The finding comes from seven years of archaeological excavations at Ceibal, a site in central Guatemala that was occupied continuously for 2,000 years. Getting to Ceibal’s origins was no small feat: The earliest buildings were buried under 23 to 60 feet (7 to 18 meters) of sediment and later construction, said study co-researcher Daniela Triadan, also a University of Arizona anthropologist.
The earliest structures recently discovered include a plaza with a western building and an eastern platform, a pattern seen at later Maya sites and also at the Olmec center of La Venta on the Gulf Coast of what is now Mexico. The researchers used radiocarbon dating to peg the date of construction to about 1000 B.C. This technique analyzes organic materials for carbon-14, an isotope or variation of carbon that decays predictably. As such, carbon-14 acts as a chemical clock archaeologists can use to figure out how long something has been in the ground.
Originally posted 2013-05-11 21:04:46. Republished by Blog Post Promoter

![20130511-225928[1]](https://coolinterestingnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/20130511-2259281-1.jpg)