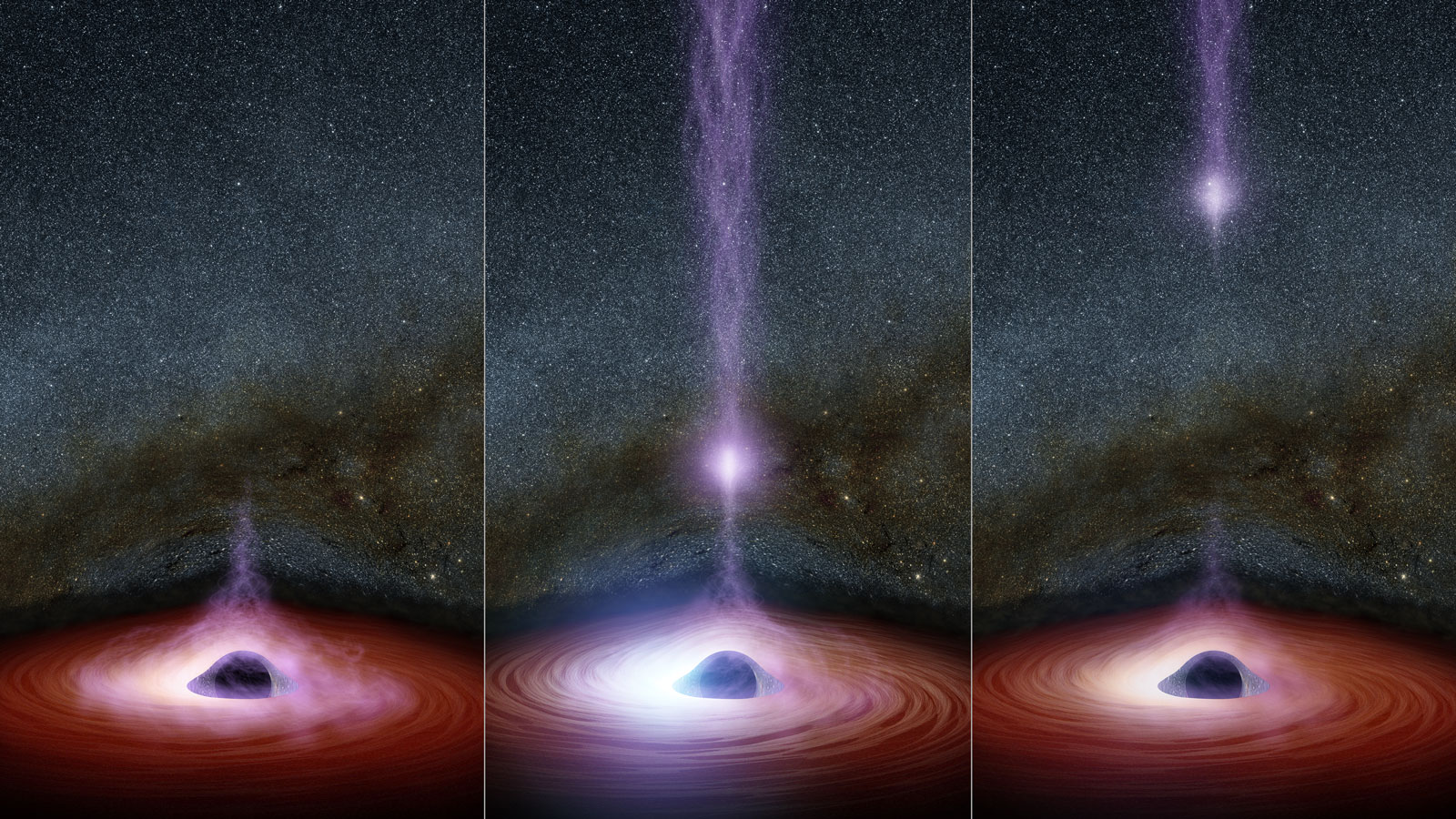
NASA’s Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) has captured an extreme and rare event in the regions immediately surrounding a supermassive black hole. A compact source of X-rays that sits near the black hole, called the corona, has moved closer to the black hole over a period of just days.
“The corona recently collapsed in toward the black hole, with the result that the black hole’s intense gravity pulled all the light down onto its surrounding disk, where material is spiraling inward,” said Michael Parker of the Institute of Astronomy in Cambridge, United Kingdom, lead author of a new paper on the findings appearing in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
As the corona shifted closer to the black hole, the gravity of the black hole exerted a stronger tug on the X-rays emitted by it. The result was an extreme blurring and stretching of the X-ray light. Such events had been observed previously, but never to this degree and in such detail.
Supermassive black holes are thought to reside in the centers of all galaxies. Some are more massive and rotate faster than others. The black hole in this new study, referred to as Markarian 335, or Mrk 335, is about 324 million light-years from Earth in the direction of the Pegasus constellation. It is one of the most extreme of the systems for which the mass and spin rate have ever been measured. The black hole squeezes about 10 million times the mass of our sun into a region only 30 times the diameter of the sun, and it spins so rapidly that space and time are dragged around with it.
Even though some light falls into a supermassive black hole never to be seen again, other high-energy light emanates from both the corona and the surrounding accretion disk of superheated material. Though astronomers are uncertain of the shape and temperature of coronas, they know that they contain particles that move close to the speed of light.
Originally posted 2015-11-22 05:32:44. Republished by Blog Post Promoter